C++写的文本颠倒代码
2013年9月23日 01:02(过程:从名为“in.txt”中读取信息,颠倒输出到“out.txt”中。)
/* C++ */
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <ctime>
int main()
{
clock_t start, finish;
start = clock();
long len = -1L; /* 与文件头的距离 */
char tmp, last; /* tmp记录当刻值,last记录上一个值 */
bool tag = false, flag = false; /* tag用于标记第二个'\n',flag用于标记汉字 */
std::ifstream inp( "in.txt", std::ios::in );
std::ofstream oup( "out.txt", std::ios::out );
if ( inp.fail() == true )
{
std::cout << "please make sure the file is exist !" << std::endl; exit( 1 );
}
inp.seekg( len, inp.end ); /* 移至文件尾 */
len = (long) inp.tellg(); /* 获取文件尾距离头的距离 */
std::cerr << "A total of " << len + 1 << " bytes\nOpening file ..."; /* 显示文件大小 */
while ( len >= 0 )
{
inp.seekg( len--, inp.beg ); /* 测试结果是:从文件头开始寻址,比从当前位置ios::cur寻址快一点. */
tmp = inp.get();
if ( tmp == 10 && !(tag ^= 1) )
continue; /* windows中‘\t’和‘\r’重复 if(flag) */
{
oup << tmp << last; /* 汉字输出 */
flag = false;
} else if ( tmp < 0 )
{
last = tmp;
flag = true;
} else
oup << tmp; /* ASCII表内值输出 */
}
inp.close();
oup.close();
finish = clock();
system( "out.txt" ); /* 打开输出文件 */
std::cerr << "\nOpen the file successfully\n";
oup.open( "run_time.txt", std::ios::app );
oup << "Time: " << (finish - start) / 1000.0 << " (s)-use beg" << std::endl; /* 在文件中写入操作时间 */
return(0);
}
注:
代码中使用从文件头开始寻址,比从当前位置ios::cur寻址快一点的原因是由于磁盘的读写方式决定的。因为,所有的寻址搜索都是文件头开始的,cur寻址先从文件头进行寻址到cur位置
再从cur寻址到偏移地址,beg从文件头通过偏移地址得到地址,所以beg要快。
//为了验证这种读写方式,请看我写的一个简单的测试过程:
为了使影响检测的因素简单化,我把上面代码中一些无关部分删除。
测试代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <ctime>
int main()
{
clock_t start, finish;
start = clock();
long len = -1L;
std::ifstream inp( "in.txt", std::ios::in );
std::ofstream oup( "out.txt", std::ios::out );
inp.seekg( len, inp.end );
len = (long) inp.tellg();
std::cerr << "A total of " << len + 1 << " bytes\nOpening file ...";
while ( len >= 0 )
{
/******使用ios::cur寻址的代码********/
oup << (char) inp.get();
inp.seekg( -2L, inp.cur ); len--;
/*******使用ios::beg寻址的代码********
* inp.seekg(len--,inp.beg);
* oup<<(char)inp.get();
************************************/
}
inp.close();
oup.close();
finish = clock();
FILE*p1 = fopen( "run_time.txt", "a+" );
fprintf( p1, "Time: %.3lf (s)-use cur\n", (double) (finish - start) / 1000.0 ); /* 牵扯格式的我比较喜欢用C */
fclose( p1 );
system( "run_time.txt" );
std::cerr << "\nOpen the file successfully\n";
return(0);
}
然后,使用一个1000000字节的文本文件测试(测试数据生成代码在最后面),测试结果如下:
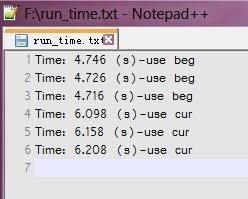
前三个是使用ios::beg寻址的,后三个是使用ios::cur寻址的,很明显前者要快一点。所以印证了我前面所说的。
附测试数据生成代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
freopen( "out.txt", "w", stdout );
long n = 1000000;
while ( n-- )
{
putchar( 65 + rand() % 26 ); /* 大写字母 */
}
return(0);
}
测试环境皆为Win XP professional,VC++6.0
文章作者: qbeenslee
